
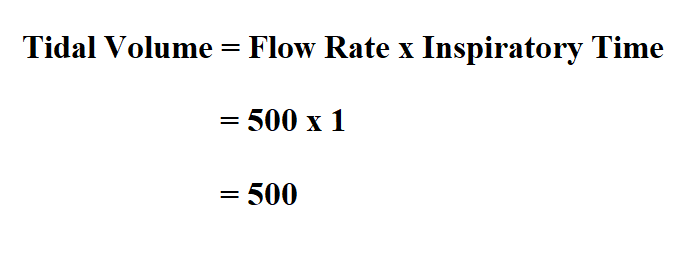
The first theories developed to explain these negative effects of mechanical. You also need to be aware that larger tidal volumes will lead to greater stretching of the alveoli as each breath goes in and out. Rats were then randomized 24 hours later to receive mechanical ventilation as a second hit, with either an injurious strategy of high tidal volume (TV) of. The consequences of high-volume ventilation, that is 10 to 15 mL/kg tidal volume, include the development of increased permeability pulmonary edema even in a previously non-injured lung ( 9) as well as increased formation of edema in the injured lung ( 10 ). So increasing the tidal volume or respiratory rate could actually reduce the minute ventilation because of the breath stacking potential.

The air from the previous breath has not been exhaled fully before the next breath, so breaths start to stack on top of one another.

This is very relevant if they are being given tidal volumes that are too large, or a respiratory rate that is too fast. However, this may also be caused by pulmonary dysfunction with an increase in dead space volume. So they might not be able to get the air out of their lungs before the next breath comes along when being mechanically ventilated. End tidal CO2 revealing a substantially low CO2 measurement also suggests hypocapnia (e.g., etCO2 << 30 mm).
#HIGH TIDAL VOLUME PLUS#
While the best sound quality (high-resolution, up to 9216 kbps) and accessibility to Dolby Atmos and Sony 360 Reality Audio tracks are exclusive to the Tidal HiFi Plus tier (£20/20/AU24 per month), Tidal doesn’t have to be more expensive than Spotify and the rest. Those patients who are suffering with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary disease (COPD), because of the physiological problems they are suffering, have problems getting the air out of their lungs. It doesn’t have to cost £20/20 per month. There maybe some situations where this rule needs some modification. If, however, you just increase the patients tidal volume with each breath, you do not increase the dead space at all. This process can increase the patients propensity to retain carbon dioxide. The problem however is that you are also increasing the amount of dead space ventilation you are giving them, as each additional breath also carries the same amount of dead space. If you do that then the ventilation of the patient will increase as every minute you are giving them additional breaths.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
